Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
What is Rackspace Spot?
Affordable, Flexible Kubernetes
Rackspace offers powerful and cost-effective managed Kubernetes solutions tailored to different needs. Rackspace Spot provides a unique way to significantly reduce costs by leveraging a dynamic Spot Market for compute capacity. This approach allows access to spare cloud resources at potentially up to 90% discount than typical fixed-rate instances.
Alongside Spot servers, On-Demand servers offers the same compute resources with traditional, predictable monthly billing and guaranteed resource availability, perfect for set and forget workloads demanding maximum stability without the need for bid management.
Spot and On-Demand server instances run within a Cloudspace, which is your fully managed Kubernetes cluster. A Cloudspace includes the managed Kubernetes control plane and can contain various server pools tailored for different workloads (general purpose, compute-heavy, memory-heavy, or GPU), utilizing either Spot or On-Demand instances.
Core Concepts Explained
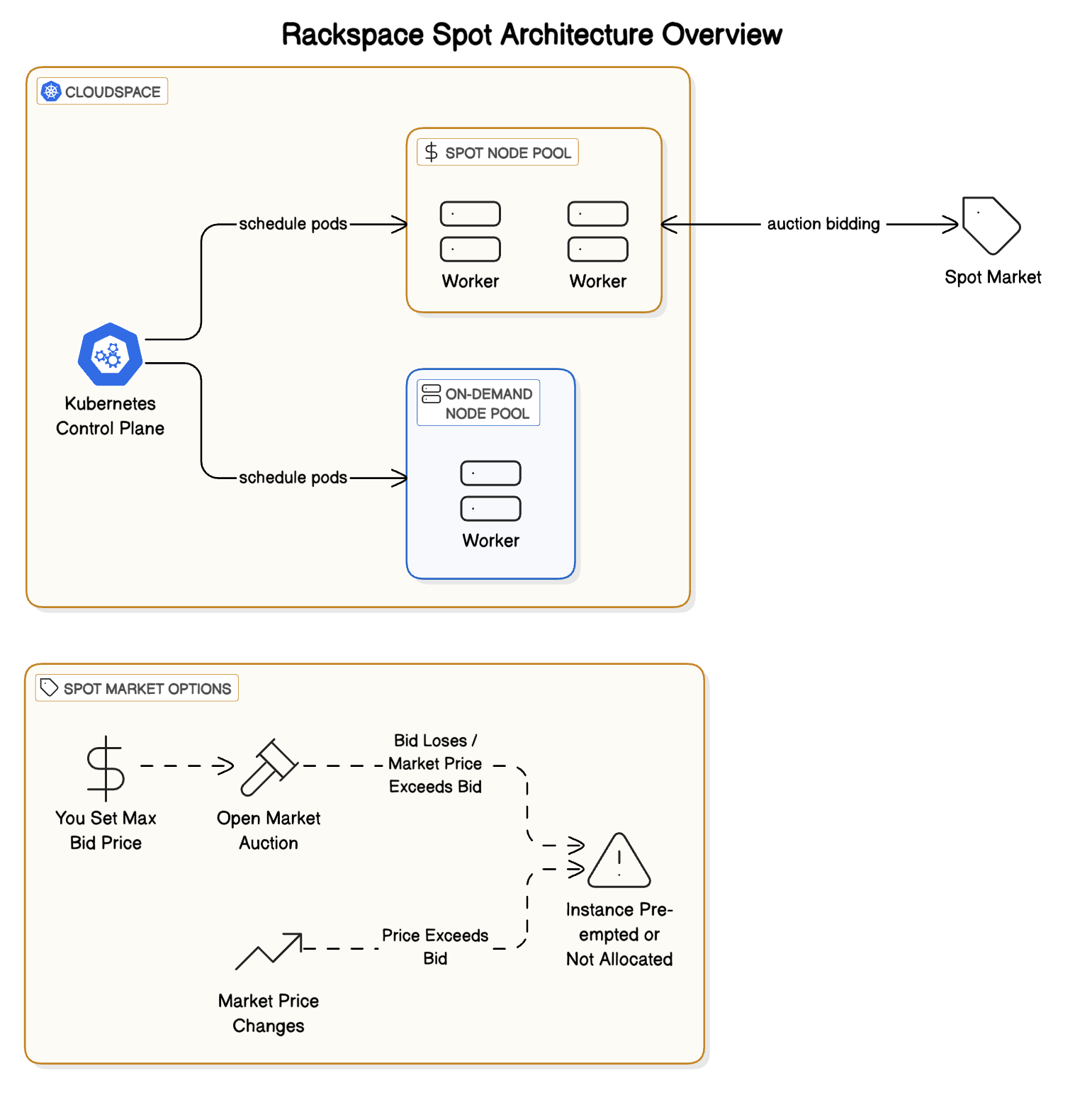
Understanding these key concepts is essential for effectively using Rackspace Spot:
- Spot Market: An automated market where the price of computing capacity fluctuates based on supply and demand. Rackspace Spot allows you to tap into this market for cost savings. Unlike some other cloud spot offerings where instances are simply reclaimed based on capacity availability alone, Rackspace Spot uses an open market auction. Your bid actively competes against others, influencing both your price and the likelihood of retaining your instance.
- Spot Instances: Kubernetes worker nodes acquired through the dynamic Spot Market. Utilizes spare capacity, meaning instances carry a risk of Pre-emption if capacity tightens or your bid is no longer competitive. This risk is manageable through bidding strategies and architectural choices. Spot instances are suitable for many production workloads when managed correctly.
- On-Demand Instances: Rackspace's traditional worker nodes offering guaranteed availability with fixed, predictable monthly pricing. These instances are not subject to the Spot Market or pre-emption, providing maximum stability.
- Pre-emption: Because Spot Instances use spare capacity, they can be reclaimed (terminated) if that capacity is needed elsewhere which is represented by market prices rising above your bid. Rackspace Spot provides tools and strategies to manage this risk. All servers that fall under Pre-emption will have a 6 minute grace period to adjust your bid before reclaim occurs. (See: Pre-emption Explained)
- Bidding: You set a maximum price you're willing to pay per hour for Spot Instances. This bid influences your access to Spot capacity and your instance's susceptibility to pre-emption. Higher bids generally reduce pre-emption risk but might increase cost slightly. (See: Bidding Best Practices)
- Hybrid Clusters: A key advantage of Rackspace's Kubernetes offerings is the ability to mix Spot Instances (to maximize cost savings on flexible or fault-tolerant workloads) and On-Demand Instances (for components requiring guaranteed uptime and stability) within the same Cloudspace. This provides a tailored balance of cost and reliability. For example, you might run your critical databases or stateful services on reliable On-Demand nodes, while using cost-effective Spot nodes for your stateless web frontends or batch processing tasks. (See: Spot vs On-Demand)
Why Use Rackspace Spot?
- Drastic Cost Reduction: Access spare compute capacity for potentially up to 90% savings compared to On-Demand pricing, significantly lowering your Kubernetes operational costs.
- Flexible Cost/Reliability Balance: Mix Spot and On-Demand nodes within a single Cloudspace to optimize costs for different parts of your application based on their tolerance for interruption.
- Standard Managed Kubernetes: Get a fully managed Kubernetes control plane and worker nodes, leveraging the standard Kubernetes API and tools (like
kubectl) you already know. Rackspace handles the Kubernetes control plane setup, upgrades, scaling, and underlying infrastructure patching, freeing you to focus on deploying and managing your applications. - Built for Modern Workloads: Ideal for stateful or stateless applications designed with fault tolerance and scalability in mind.
Suitable Use Cases for Spot Instances
Spot Instances are particularly well-suited for workloads that are:
- Fault-tolerant: Applications designed to handle interruptions gracefully, perhaps by checkpointing progress or having replicas running elsewhere.
- Stateless: Services that don't store critical state locally on the node, making replacement easier.
- Flexible in Completion Time: Jobs that don't have strict, immediate deadlines.
- Scalable: Applications that can easily scale horizontally by adding or removing nodes.
Examples:
- Batch Processing & Big Data: Large-scale data analysis (Spark, Dask), scientific simulations, rendering jobs where interruptions can be managed and work can be redistributed.
- CI/CD Pipelines: Running build agents and testing environments where ephemeral nodes are acceptable and cost savings are beneficial.
- Development & Staging Environments: Providing cost-effective environments for developers that mimic production but don't require the same uptime guarantees.
- Stateless Web Applications/APIs: Scaling out the front-end or API layers of applications that can handle node loss, often used in combination with On-Demand nodes for core services.
- Machine Learning Training: Training ML models, especially tasks that can be checkpointed and resumed.
Workloads less suitable for only Spot Instances (Consider On-Demand or Hybrid approaches):
- Critical Databases: Primary databases requiring constant uptime and data persistence.
- Stateful Applications: Applications that store essential state on the node and cannot easily tolerate interruptions (e.g., message queues without high availability setups).
Rackspace Spot offers significant cost savings by using dynamically priced spare capacity, but requires managing the potential risk of instance pre-emption through bidding. Hybrid clusters combining Spot and On-Demand nodes offer a powerful way to balance cost and reliability.
By understanding these concepts and trade-offs, you can strategically use Rackspace Spot to achieve significant cost savings while running robust Kubernetes applications. Explore the linked sections for deeper dives into managing pre-emption and optimizing your bidding strategy.
© 2023 RACKSPACE TECHNOLOGY